-
Introduction
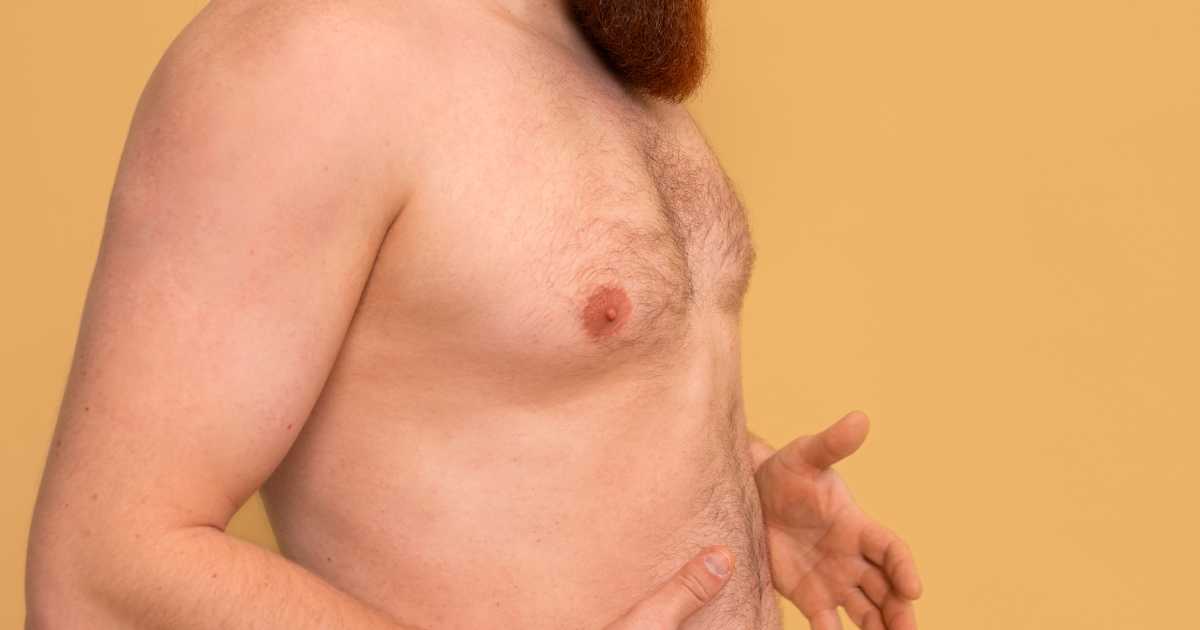
Male gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It is a relatively common condition that can occur during different stages of life, such as puberty or adulthood. Male gynecomastia can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress, leading individuals to seek medical evaluation and treatment.

-
Causes of Male Gynecomastia
Several factors can contribute to the development of gynecomastia in males:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Gynecomastia arises due to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels. Estrogen stimulates breast tissue growth, while testosterone promotes masculine characteristics. If there is an increase in estrogen or a decrease in testosterone, it can lead to the enlargement of breast tissue.
- Puberty: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common, and gynecomastia can occur as a result. In many cases, it resolves on its own within a few months to a couple of years.
- Aging: As men age, there can be changes in hormone levels. The ratio of estrogen to testosterone may increase, leading to the development of gynecomastia.
- Medications: Certain medications can contribute to gynecomastia as a side effect. These may include some anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, certain antidepressants, and certain chemotherapy drugs.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypogonadism, hyperthyroidism, liver disease, and tumors of the testes or adrenal glands, can cause hormonal imbalances that result in gynecomastia.
-
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Male Gynecomastia
The primary symptom of male gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue. Other symptoms may include breast tenderness or pain and, in some cases, nipple discharge. It is essential to differentiate gynecomastia from other conditions that can cause breast enlargement, such as breast cancer.
To diagnose male gynecomastia, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough medical history and physical examination. They may also perform blood tests to assess hormone levels and rule out underlying medical conditions. In some cases, imaging tests such as mammograms or ultrasounds may be recommended.
-
Treatment Options for Male Gynecomastia
The treatment for male gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In cases where gynecomastia is mild and not causing significant distress, observation and monitoring may be sufficient. If a specific medication is contributing to gynecomastia, the doctor may consider changing or discontinuing it if feasible.
In cases where gynecomastia persists or causes psychological distress or physical discomfort, various treatment options are available:
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy, such as anti-estrogens or testosterone replacement therapy, may be prescribed to restore the hormonal balance and reduce breast tissue enlargement.
- Surgery: Male breast reduction surgery, also known as gynecomastia surgery, may be an option for individuals with severe gynecomastia. The surgical procedure involves removing excess breast tissue and reshaping the chest for a more masculine appearance.
-
Conclusion
Male gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in males and can occur during different stages of life. It is often caused by hormonal imbalances, medications, or underlying medical conditions. While mild cases may not require treatment, medical evaluation is crucial to determine the underlying cause and address any physical or psychological concerns. Treatment options include observation, medication-based therapies, and surgery. If you are experiencing changes in your breast tissue, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
